5G IoT Edge Computing is reshaping how organizations process data at the source, enabling near-instant insights as devices, networks, and applications converge. With 5G technology delivering ultra-low latency and high reliability, IoT devices can feed streams to edge analytics and stay synchronized across the field. This shift unlocks edge computing benefits such as real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and smarter decision-making, especially in industrial IoT environments. By bringing computation closer to where data is produced, organizations reduce bandwidth use, improve privacy, and strengthen IoT security, while expanding edge computing use cases in manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare. As businesses pursue smarter operations and enhanced customer experiences, understanding how these technologies interact will be crucial for modern digital strategy.
Viewed through a different lens, this convergence is about distributed computing at the edge of the network, where data is processed close to the source rather than in distant data centers. You might hear it described as near-edge processing, on-site analytics, or multi-access edge computing (MEC) in modern architectures. The emphasis is on reducing round-trip times, preserving bandwidth for critical tasks, and enabling dynamic, context-aware applications. By framing the same trend with terms like fog computing, localized intelligence, and edge-centric orchestration, teams can map use cases across industrial, urban, and energy domains. In practice, organizations adopt a layered approach that places compute, storage, and security controls closer to operations, while still leveraging the cloud for deeper insights.
5G IoT Edge Computing: Real-Time Decisions at the Edge
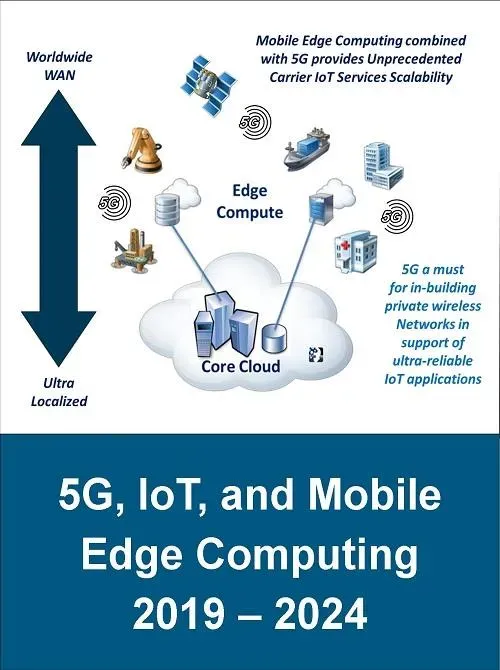
The convergence of 5G technology, IoT, and edge computing enables data to be captured, transmitted, and analyzed in near real-time at the network edge. With 5G technology features like ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), network slicing, and massive device connectivity, IoT sensors can deliver streams that edge compute nodes readily process. This reduces latency, lowers backhaul demands, and supports edge analytics that power faster operational decisions across manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare.
Edge computing benefits are most evident in industrial IoT deployments where time-sensitive data drives automated actions, quality control, and predictive maintenance. Processing data locally on the shop floor or at remote sites can minimize downtime, improve customer experiences, and preserve privacy by keeping sensitive information closer to the source. By leveraging edge computing use cases such as asset monitoring and real-time risk detection, organizations can unlock more resilient and efficient operations.
Security, Architecture, and Governance for 5G IoT Edge in Industrial IoT
Architectural patterns for 5G IoT Edge include a layered setup of edge devices, gateways, edge compute nodes, and a central cloud for orchestration. Data from IoT devices is filtered and pre-processed at the edge, enabling swift responses in time-critical scenarios. Deployment considerations cover edge hardware choices, containerized software, and edge orchestration platforms, with attention to performance targets, security, and scalability that support edge computing use cases across industrial environments.
IoT security and governance at the edge are essential to prevent data leakage and ensure regulatory compliance. A defense-in-depth approach—secure boot, firmware integrity checks, encryption in transit and at rest, device identity, and zero-trust access controls—helps safeguard edge nodes and gateways. Establishing data ownership, data sovereignty, and consistent security policies across distributed sites ensures the 5G IoT Edge ecosystem remains trustworthy and auditable, enabling sustainable industrial automation and digital transformation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key edge computing benefits of 5G IoT Edge Computing for industrial IoT deployments?
5G IoT Edge Computing enables on-site processing by bringing computing, storage, and analytics closer to sensors and machines in industrial environments. This reduces latency, lowers backhaul bandwidth, and supports real-time decision‑making for predictive maintenance, quality control, and automation. It also enhances reliability when cloud connectivity is limited and improves data governance by keeping sensitive data at the edge, while supporting scalable deployment through secure edge infrastructure. In short, the edge computing benefits include faster responses, cost savings, and more resilient industrial operations.
How do 5G technology and IoT security shape edge computing use cases across industries?
5G technology provides the high-speed, low-latency connectivity and features like network slicing that enable real-time edge analytics for diverse use cases. IoT security at the edge is essential, covering device identity, encrypted data in transit and at rest, secure boot, and zero-trust access controls to prevent breaches. Together, these factors enable edge computing use cases such as remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, autonomous operations, and smart city or healthcare applications, where fast, local processing improves safety and efficiency.
| Area | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Understanding the players: 5G, IoT, and edge computing |
|