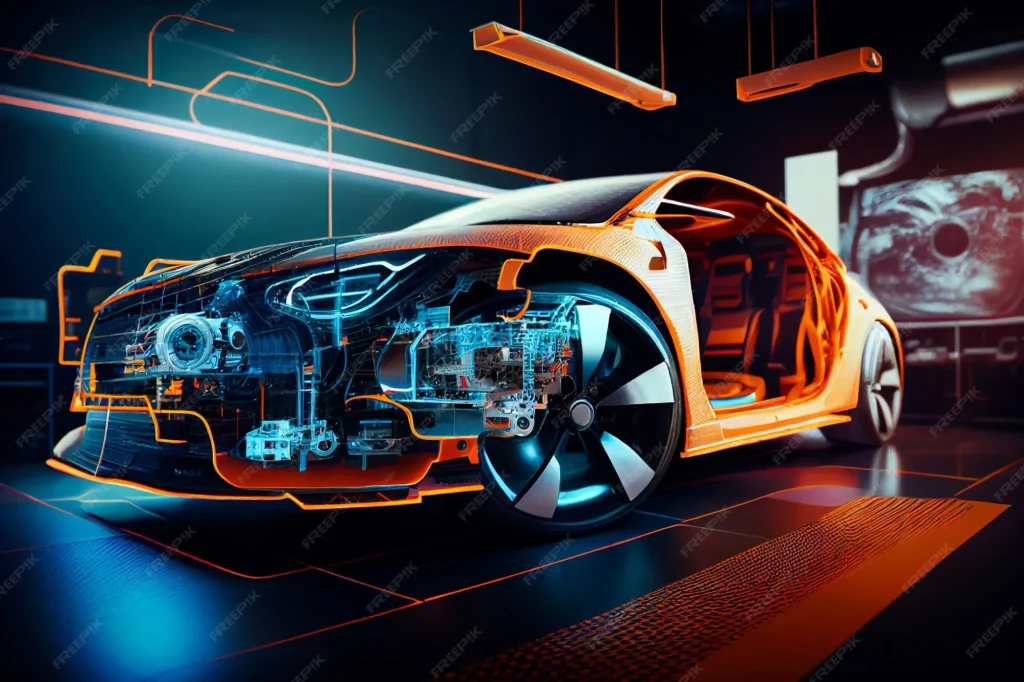
Automobile innovations are reshaping the way we move, work, and interact with our surroundings. From propulsion breakthroughs to smarter safety features, this shift drives efficiency higher and travel experiences richer. Electric vehicles are becoming mainstream options for individuals and fleets, driven by better batteries, faster charging, and longer ranges. Meanwhile, advanced connectivity keeps cars in sync with services, infrastructure, and other vehicles, enabling smarter maintenance and routing. These advances, coupled with evolving policies and consumer demand, set the stage for safer journeys and broader adoption of modern mobility.
Beyond the terms used in headlines, the topic unfolds through ideas like self-driving technology, AI-powered mobility, and data-enabled vehicle ecosystems. Vehicles increasingly rely on sensor fusion, on-board software, and cloud services to deliver safer, more efficient journeys. The focus shifts from single inventions to integrated platforms where propulsion, sensing, and connectivity cooperate to transform daily commuting. In this lens, autonomous driving capabilities, smart infrastructure, and tailored mobility services outline a future where neighborhoods move more smoothly and sustainably.
Automobile innovations: powering electric propulsion for sustainable mobility
Automobile innovations are accelerating the transition to electric propulsion and sustainable mobility by advancing electric vehicles (EVs), energy storage, and charging ecosystems. Breakthroughs in lithium‑ion and solid‑state batteries raise energy density, extend range, and shorten charging times, while smarter thermal management and regenerative braking maximize efficiency in real-world driving. As charging networks expand and modular battery packs become commonplace, consumers gain practical, cost‑effective options that reduce fuel costs and emissions. These developments position electric vehicles as central to a cleaner, more efficient transportation future.
Beyond the battery itself, automobile innovations encompass grid-aware and consumer‑friendly charging strategies, standardized interfaces, and better vehicle-to-grid integration. Smart charging aligns energy use with renewable generation and grid capacity, supporting sustainable mobility at scale. As shoppers compare EV models, the emphasis on electric vehicles, charging convenience, and lifecycle emissions becomes a key differentiator, underscoring how automotive R&D is reshaping ownership models and accelerating broad adoption.
Connectivity, autonomy, and safety: shaping the connected car era with advanced safety features
Connectivity and data play central roles in modern vehicle design, enabling in‑vehicle experiences and a plethora of services that extend beyond the drive. Connected car technology streams navigation, entertainment, predictive maintenance, and real‑time traffic data to passengers and fleets, while OTA updates keep software current without dealer visits. This connectivity also supports new mobility models—on‑demand services and fleet optimization—through data analytics, vehicle‑to‑everything communication, and cloud services, all of which enhance safety, efficiency, and convenience.
Autonomous driving and advanced safety features are core components of this evolution. Driver‑assistance systems—adaptive cruise control, lane‑keeping, automatic emergency braking, and traffic sign recognition—progress along a continuum toward higher levels of automation as perception, localization, and decision‑making algorithms mature. Alongside autonomy, advanced safety features such as improved airbags, occupant monitoring, and robust cybersecurity measures work together to reduce risk, boost driver confidence, and transform daily urban travel into safer, more productive journeys.
Frequently Asked Questions
How are electric vehicles and advances in battery technology shaping efficiency, charging, and ownership costs in modern mobility?
Electric vehicles rely on high-energy-density batteries (lithium-ion and solid-state) that enable longer range and better efficiency through improved energy density, regenerative braking, and thermal management. Faster charging and wider charging networks—plus smart charging that aligns with grid capacity and renewable energy—make daily charging convenient and economical, supporting sustainable mobility. As battery costs continue to fall and maintenance needs stay low, the total cost of ownership for electric vehicles becomes more competitive with traditional combustion vehicles.
How do autonomous driving and connected car technology reinforce advanced safety features to improve safety and the in-car experience?
Autonomous driving relies on advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) like adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping, automatic emergency braking, and precise perception, localization, and decision-making to improve safety. Connected car technology enables over-the-air updates, real-time data sharing, cloud services, and secure communications, enhancing performance and safety features while enabling richer in-car experiences. Together, these innovations create safer journeys, continuous software improvements, and smarter mobility, while addressing cybersecurity and privacy considerations.
| Aspect | Summary |
|---|---|
| Electric propulsion and energy efficiency | EVs have moved from niche to mainstream due to advances in batteries (lithium‑ion and solid‑state), higher energy density, faster charging, and cost declines. Real‑world efficiency is boosted by regenerative braking, thermal management, and driving modes. A broader ecosystem—charging standards, grid infrastructure, and smart charging—supports practicality and lower emissions. |
| Autonomy and safety | Autonomous driving and ADAS are central to Automobile innovations. Features like adaptive cruise control, lane‑keeping, automatic emergency braking, and traffic sign recognition progressively shift control toward software. Reliable perception, localization, decision‑making, and secure V2X communication are essential as automation levels rise. |
| Connectivity, data, and the in‑car experience | Connected car technology enables data collection, predictive maintenance, OTA updates, and cloud services for navigation and entertainment. This fuels new mobility models (on‑demand services, fleets, smart city integration) while underscoring the need for cybersecurity and privacy protections and intuitive human‑machine interfaces. |
| Materials, efficiency, and sustainability | Manufacturing and materials choices (high‑strength steels, aluminum, composites) reduce weight and emissions. Recycling and circular economy principles guide material selection and lifecycle considerations. Sustainable mobility concepts and shared ownership are pursued to minimize energy use and environmental impact. |
| The road ahead: infrastructure, policy, and consumer adoption | Policy alignment, standards, and investment in infrastructure (charging networks, smart grids, urban redesign) are required for widespread adoption. Affordability, reliability, service networks, insurance shifts, and regulatory frameworks shape consumer uptake and safety in a connected, automated mobility future. |
Summary
Conclusion