Automobile safety features have evolved from basic protections to sophisticated, proactive systems that actively reduce risk on every drive. As vehicles become smarter and more connected, car safety features and vehicle safety technology work together to prevent crashes. This introductory guide highlights how automatic emergency braking and lane departure warning contribute to safer travel. Understanding these capabilities helps readers prioritize what to look for when shopping for a new car. From sensors and intelligent algorithms to reinforced crash structures, modern safety measures provide a layered shield for occupants on every road.
Beyond the exact terms, the topic expands into protective car technologies and driver-assist systems that quietly monitor distance, speed, and surroundings. This LSI-driven framing groups forward-looking capabilities under crash-avoidance, occupant protection, and sensor fusion, using alternative descriptors to connect related ideas such as forward-collision alerts, adaptive cruise control, blind-spot monitoring, and automated braking. The aim is to illuminate how these technologies reduce risk and injuries through coordinated sensing, processing, and actuation, even before a human reacts. As connectivity and AI advance, vehicle safety concepts like V2X communication, intelligent restraint systems, and autonomous safety features are likely to become standard in the coming years.
Automobile Safety Features and Vehicle Safety Technology: How Modern Cars Protect You
Automobile safety features have transformed from basic protections to advanced, proactive systems that actively reduce risk on every drive. They now blend active safeguards with passive protections to create a layered safety net that shields drivers, passengers, and pedestrians, especially as vehicles become smarter and more connected. This evolution in car safety features is powered by advances in vehicle safety technology, sensor fusion, and sophisticated design, enabling safer travel without demanding extra attention from the driver.
In the realm of car safety features, you’ll hear terms like car safety features, vehicle safety technology, automatic emergency braking, airbags and seat belts, and lane departure warning. These terms describe components and systems that collectively raise safety standards across the automotive industry. Active safety features aim to prevent crashes, while passive safety features cushion impacts, and modern vehicles increasingly blend both to deliver safer journeys on every road.
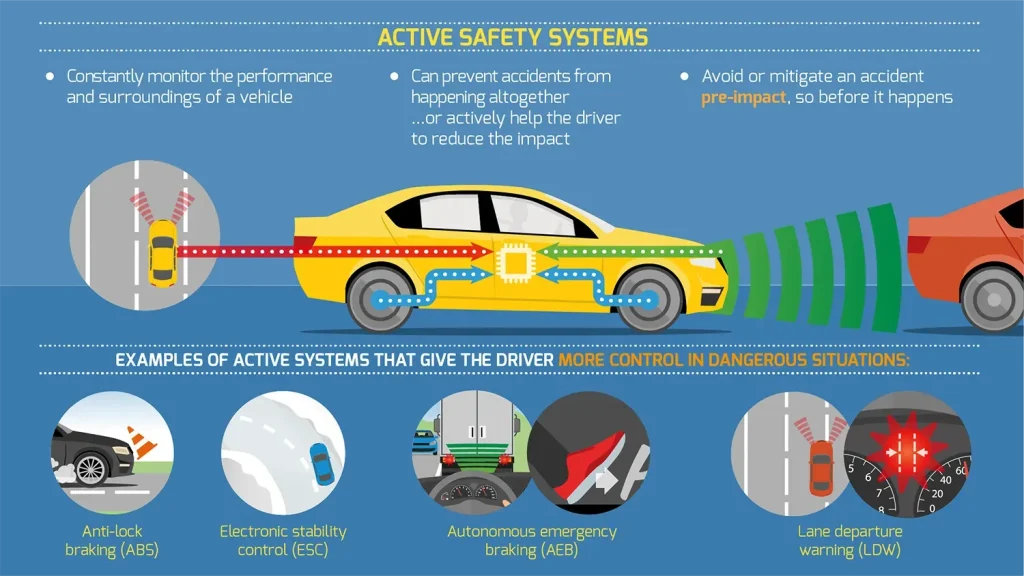
Car Safety Features Essentials: From Automatic Emergency Braking to Lane Departure Warning
Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) is a cornerstone of modern vehicle safety technology. Using forward sensors, cameras, and sometimes radar, AEB detects a potential collision with a vehicle, pedestrian, or object ahead and automatically applies the brakes if the driver does not respond quickly enough. When implemented effectively, AEB can significantly reduce rear-end crashes and mitigate injury severity by lowering impact speed, illustrating how automobile safety features translate into real-world life-saving outcomes.
Lane Departure Warning (LDW) and Lane Keeping Assist (LKA) help keep drivers within their lanes, reducing the risk of drifting into adjacent lanes or off the roadway. These systems often pair with Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) and Blind-Spot Monitoring (BSM) to create a comprehensive safety package that reduces driver workload while maintaining situational awareness. In addition to these active measures, passive protections—such as airbags and seat belts—along with a reinforced passenger cell, remain essential for minimizing injuries when a crash cannot be avoided.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Automobile safety features, and how do car safety features and vehicle safety technology work to prevent crashes?
Automobile safety features include both active systems that prevent crashes and passive protections that reduce injury when a collision occurs. Active safety features—such as Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB), Lane Departure Warning (LDW) and Lane Keeping Assist (LKA), Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC), Blind-Spot Monitoring (BSM), and Rear Cross-Traffic Alert (RCTA)—use sensors and software to detect hazards, maintain safe distances, and help you avoid a crash. Passive protections—airbags and seat belts, crumple zones, reinforced passenger cell, side-impact protection, and head restraints—shield occupants if a collision happens. Together, these car safety features and other vehicle safety technology form a layered safety strategy that can save lives.
What should I prioritize when shopping for a new car to get the most from Automobile safety features, including car safety features and vehicle safety technology?
Prioritize a balanced safety package that combines active safety (AEB, LDW/LKA, ACC, BSM/RCTA) with robust passive protection (multiple airbags, strong passenger cell). For urban driving, emphasize LDW, BSM, and RCTA; for highway trips, AEB and ACC reduce fatigue and crash risk. Look for models with diverse sensors (cameras, radar, lidar where available) to maintain reliability in challenging conditions, and check official safety ratings (NHTSA, Euro NCAP, IIHS) as real-world indicators. This approach aligns with the broader concept of automobile safety features and vehicle safety technology and helps you choose a safer vehicle.
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Active Safety Features | Technologies designed to prevent crashes and assist drivers, including automatic emergency braking, lane warning/keeping, adaptive cruise control, and cross-traffic alerts. |
| Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) | Uses forward sensors to detect potential collisions and automatically apply brakes to reduce impact and injury risk. |
| Lane Departure Warning (LDW) & Lane Keeping Assist (LKA) | Monitors lane markings to warn when drifting; LKA can steer back toward the lane center if needed. |
| Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) & Traffic Jam Assist | Maintains safe following distance and can manage stop-and-go traffic to reduce driver workload and prevent rear-end crashes. |
| Blind-Spot Monitoring (BSM) & Rear Cross-Traffic Alert (RCTA) | Detects vehicles in blind spots and cross traffic when reversing to prevent unsafe lane changes. |
| Passive Safety Features | Protections that cushion impact and protect occupants when a crash occurs, such as airbags, seat belts, crumple zones, reinforced passenger cell, side-impact protection, and head restraints. |
| Airbags & Seat Belts | Critical life-saving restraints and cushions that cooperate to reduce injury severity. |
| Crumple Zones & Reinforced Passenger Cell | Designed to absorb energy and maintain survivable space for occupants during a collision. |
| Side-Impact Protection & Head Restraints | Structural reinforcements and restraints that reduce injuries from side impacts and whiplash. |
| Choosing the Right Safety Package | Evaluates features for common crash scenarios, balancing active and passive protections, and considering driving environment and risk profile. |
| Regulatory Standards & Safety Ratings | Ratings from NHTSA, Euro NCAP, and IIHS help buyers compare models based on safety features and crash performance. |
| The Future of Automobile Safety Features | Connectivity, V2V/V2X, and AI-driven safety interventions are shaping proactive safety and more autonomous capabilities. |
Summary
Conclusion: A Safer Road Ahead
Automobile safety features form the backbone of modern road safety. By combining active safety technologies like automatic emergency braking, lane departure warning, and adaptive cruise control with robust passive protections such as airbags and crumple zones, today’s cars offer a tiered shield against crashes and injuries. For drivers, understanding the spectrum of car safety features and vehicle safety technology helps make informed decisions about which features align with daily needs and risk profiles. As regulation, testing, and innovation continue to advance, the safety gains from automobile safety features will only increase, contributing to safer journeys and saving more lives on every road.